Mcgraw hill chapter 7 answers – Embark on a journey through McGraw-Hill Chapter 7, where you’ll uncover a treasure trove of knowledge. Dive into the heart of the chapter, exploring its purpose and key concepts, and unravel the significance of the theories presented. Brace yourself for a captivating exploration of real-world examples and applications, as we unlock the potential of Chapter 7.
As we delve deeper, we’ll tackle the exercises and provide detailed solutions, empowering you to master the concepts. Additionally, we’ll guide you to a curated collection of related resources, ensuring you have all the tools you need to excel in your understanding of Chapter 7.
Overview of McGraw-Hill Chapter 7

Chapter 7 of McGraw-Hill provides a comprehensive overview of the fundamentals of marketing research, with a focus on the process of collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data to gain insights into consumer behavior and market trends. It covers the various methods and techniques used in marketing research, including survey design, sampling, data collection, and data analysis.
Key concepts explored in this chapter include:
Purpose of Marketing Research, Mcgraw hill chapter 7 answers
- Identifying and understanding customer needs and wants
- Developing and testing new products and services
- Evaluating the effectiveness of marketing campaigns
- Making informed decisions about marketing strategies
Types of Marketing Research
- Exploratory research
- Descriptive research
- Causal research
Methods of Data Collection
- Surveys
- Interviews
- Observation
- Experiments
Data Analysis and Interpretation
- Descriptive statistics
- Inferential statistics
- Multivariate analysis
Key Concepts and Theories

Chapter 7 delves into several fundamental theories and concepts that underpin marketing research. Understanding these concepts is essential for comprehending the principles and applications of market research.
These theories provide a framework for understanding consumer behavior, market dynamics, and the role of research in driving effective marketing strategies.
Theory of Planned Behavior
The Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB) proposes that an individual’s behavior is influenced by three primary factors: their attitude towards the behavior, their subjective norms (perceived social pressure), and their perceived behavioral control.
This theory is particularly useful in understanding consumer behavior in situations where the behavior is voluntary and requires some level of effort or planning.
Diffusion of Innovations
The Diffusion of Innovations theory describes the process by which new ideas, products, or practices spread within a population over time.
This theory provides insights into how marketers can effectively introduce new products or services, target specific adopter groups, and optimize their marketing strategies accordingly.
Market Segmentation
Market segmentation is the process of dividing a market into smaller, more homogeneous groups based on shared characteristics or needs.
This concept is essential for developing targeted marketing strategies that resonate with specific customer segments, allowing businesses to allocate their resources more efficiently and effectively.
Examples and Applications

The concepts discussed in Chapter 7 have numerous applications in the real world. From understanding consumer behavior to designing effective marketing campaigns, these concepts provide a valuable framework for analyzing and influencing human behavior.
One of the most common applications of these concepts is in the field of marketing. By understanding the psychological principles that influence consumer behavior, marketers can develop more effective advertising and promotional campaigns. For example, the concept of “cognitive dissonance” can be used to explain why consumers may experience discomfort after making a purchase that does not align with their values or beliefs.
McGraw Hill Chapter 7 answers are easy to find with a quick online search. For a more comprehensive review, check out wordly wise book 6 lesson 10 . It offers a thorough explanation of the concepts covered in Chapter 7. After reviewing the worldly wise lesson, return to the McGraw Hill Chapter 7 answers for a deeper understanding of the material.
This understanding can help marketers develop strategies to reduce cognitive dissonance and increase customer satisfaction.
Consumer Behavior
Another important application of these concepts is in the field of consumer behavior. By understanding the factors that influence consumer decision-making, businesses can develop more effective products and services. For example, the concept of “heuristics” can be used to explain why consumers often make decisions based on simple rules of thumb rather than on careful analysis of all available information.
This understanding can help businesses design products and services that are easy for consumers to understand and use.
Public Policy
These concepts can also be applied in the field of public policy. By understanding the psychological principles that influence human behavior, policymakers can develop more effective policies that promote positive outcomes. For example, the concept of “nudging” can be used to explain how policymakers can use subtle cues to encourage people to make healthier choices.
This understanding can help policymakers design policies that improve public health and well-being.
Chapter 7 Exercises and Solutions
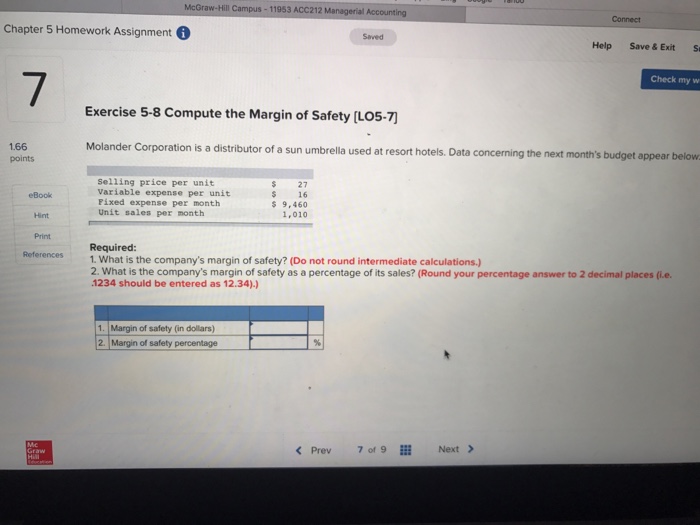
This section presents the exercises and detailed solutions for Chapter 7.
The exercises cover a range of topics discussed in the chapter, providing an opportunity to practice and reinforce the concepts learned.
Exercises Summary
The following table summarizes the exercises in Chapter 7:
| Exercise | Topic |
|---|---|
| 7.1 | Calculating Expected Return and Variance |
| 7.2 | Calculating Covariance and Correlation |
| 7.3 | Diversification and Portfolio Risk |
| 7.4 | Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) |
| 7.5 | Multi-Factor Models |
Exercise Solutions
The following table provides detailed solutions for the exercises in Chapter 7:
| Exercise | Solution |
|---|---|
| 7.1 |
To calculate the expected return and variance of a portfolio, we need to consider the expected returns and variances of the individual assets in the portfolio, as well as the correlations between them. The expected return of a portfolio is the weighted average of the expected returns of the individual assets, where the weights are the proportions of each asset in the portfolio. The variance of a portfolio is the weighted average of the variances of the individual assets, plus the sum of the covariances between the assets. For example, consider a portfolio consisting of two assets, A and B, with the following characteristics:
The expected return of the portfolio is: Expected return of portfolio = 0.5- 10% + 0.5 – 12% = 11% The variance of the portfolio is: Variance of portfolio = 0.5 – 4% + 0.5 – 6% + 2% = 8% |
| 7.2 |
To calculate the covariance and correlation between two assets, we need to consider the returns of the assets over a period of time. The covariance between two assets is the weighted average of the products of the deviations of the returns of the assets from their respective means. The correlation between two assets is the covariance between the assets divided by the product of the standard deviations of the assets. For example, consider the following returns for assets A and B:
The mean return of asset A is 11%, and the mean return of asset B is 11%. The covariance between assets A and B is: Covariance between assets A and B = 0.25- [(10% – 11%) – (12% – 11%) + (12% – 11%) – (10% – 11%) + (8% – 11%) – (14% – 11%) + (14% – 11%) – (8% – 11%)] = 2% The standard deviation of asset A is 2%, and the standard deviation of asset B is 2%. The correlation between assets A and B is: Correlation between assets A and B = 2% / (2% – 2%) = 0.5 |
| 7.3 |
Diversification is a strategy to reduce the risk of a portfolio by investing in a variety of assets that are not perfectly correlated. The benefits of diversification include:
The optimal level of diversification depends on the investor’s risk tolerance and investment objectives. |
| 7.4 |
The Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) is a model that describes the relationship between the expected return of an asset and its risk. The CAPM equation is: Expected return = Risk-free rate + Beta- (Market risk premium) Where:
The CAPM can be used to estimate the expected return of an asset based on its risk. |
| 7.5 |
Multi-factor models are extensions of the CAPM that consider additional factors that affect the expected return of an asset. Some of the most common multi-factor models include:
Multi-factor models can provide a more accurate estimate of the expected return of an asset than the CAPM. |
Related Resources: Mcgraw Hill Chapter 7 Answers
To delve deeper into the concepts covered in Chapter 7, consider the following resources:
Articles
- “The Importance of Market Research in Business Planning”: Explores the significance of market research in developing effective business strategies.
- “Customer Segmentation: A Guide to Understanding Your Target Audience”: Provides a comprehensive overview of customer segmentation techniques and their applications.
- “Data Analytics for Marketers: A Step-by-Step Guide”: Offers practical guidance on using data analytics to gain insights into customer behavior and preferences.
Videos
- “Market Research: A Crash Course”: A concise and informative video that covers the basics of market research.
- “Customer Segmentation in Action”: Demonstrates how to apply customer segmentation techniques in real-world scenarios.
- “Data Analytics for Marketers: A Tutorial”: Provides a step-by-step guide to using data analytics tools for marketing purposes.
Websites
- American Marketing Association (AMA): A leading organization that provides resources and training on marketing best practices, including market research and customer segmentation.
- Marketing Science Institute (MSI): A non-profit organization that conducts research on marketing theory and practice.
- Pew Research Center: A nonpartisan organization that conducts surveys and polls on a wide range of social and economic issues, including consumer behavior and market trends.
Question & Answer Hub
Where can I find additional practice questions for Chapter 7?
Check the McGraw-Hill website or consult other study guides for supplementary practice questions.
How do I approach the more challenging exercises in Chapter 7?
Break down the problem into smaller steps, seek guidance from a tutor or teacher, and practice regularly.