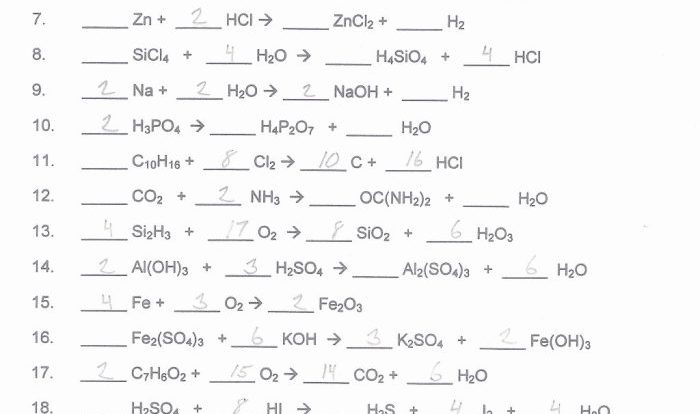
Balance the equations by inserting coefficients as needed. – Balancing chemical equations is a crucial skill in chemistry that ensures the conservation of mass and charge. This guide will provide a comprehensive overview of how to balance equations by inserting coefficients, offering step-by-step instructions, tips, and examples to empower readers with this essential technique.
By delving into the concepts of balancing equations and the role of coefficients, this guide aims to equip readers with the knowledge and skills necessary to tackle chemical equations with confidence and accuracy.
Balancing Equations: Balance The Equations By Inserting Coefficients As Needed.

Balancing chemical equations involves adjusting the stoichiometric coefficients of reactants and products to ensure that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides of the equation. This ensures that the law of conservation of mass is upheld, as atoms are neither created nor destroyed during a chemical reaction.
Inserting Coefficients, Balance the equations by inserting coefficients as needed.
To balance equations, coefficients are inserted in front of chemical formulas. These coefficients represent the number of molecules or moles of each substance involved in the reaction. To determine the correct coefficients, follow these steps:
- Start by balancing the most complex molecule or ion.
- Balance each element one at a time, working from left to right.
- Adjust coefficients until the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides.
- Check that the overall charge is balanced if the equation involves ions.
Using HTML Table Tags
HTML table tags can be used to organize and present balanced equations in a clear and concise manner. To create a table, use the
| tag. For example:
“`html
“` Examples and MethodsHere are some examples of balancing equations using coefficients:
Different methods can be used for balancing equations, including:
Advanced ApplicationsBalancing equations is essential in various advanced applications, such as:
Questions Often AskedWhat is the purpose of balancing chemical equations? Balancing chemical equations ensures that the number of atoms of each element on the reactants’ side equals the number of atoms of that element on the products’ side, adhering to the law of conservation of mass. How do I determine the correct coefficients to balance an equation? Start by balancing the most complex molecule or ion, then balance the remaining elements one at a time. Use trial and error to find the smallest whole-number coefficients that balance the equation. Can I use decimals or fractions as coefficients? No, coefficients must be whole numbers. If you obtain a fraction or decimal, multiply the entire equation by a number that will eliminate the fraction or decimal. 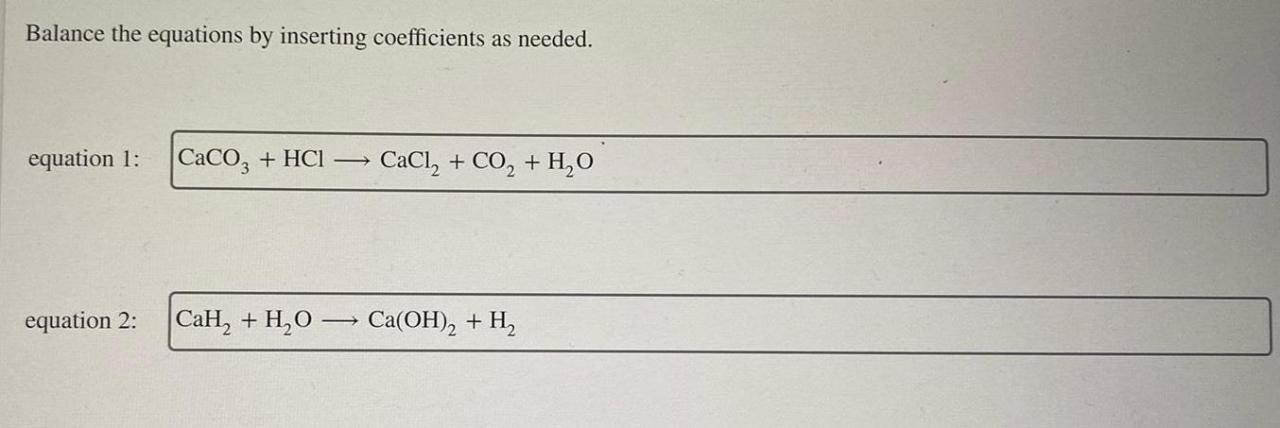 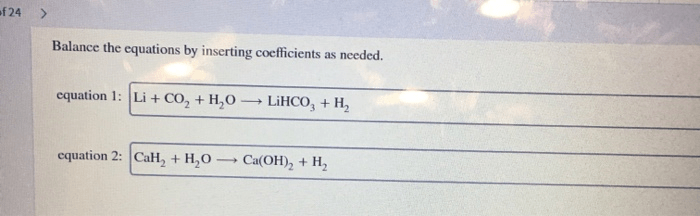  |